Eye Injury And Infections
8/9/2021
Last week we learned about vision development, vision issues and congenital or developed eye conditions. Today we are going to learn about eye injuries and infections. We will discuss different diagnoses, symptoms, treatment, when to seek emergency care, and first aid treatment.
EYE INJURIES AND INFECTIONS
Eye injury and infection can seriously impact vision, if your child has an injury or infection, they may need be evaluated by your provider and possibly an ophthalmologist. Infection can escalate and vision changes can happen quickly with injuries.
INJURIES
If your child injures their eye, seek treatment as soon as possible. Directly after the injury:
• Do not remove debris or a foreign object just encourage blinking
• Do not apply any medications or ointments that are not medically advised
• Do not apply pressure or rub
• Do not flush unless there is known chemical exposure
• Cover the eye gently
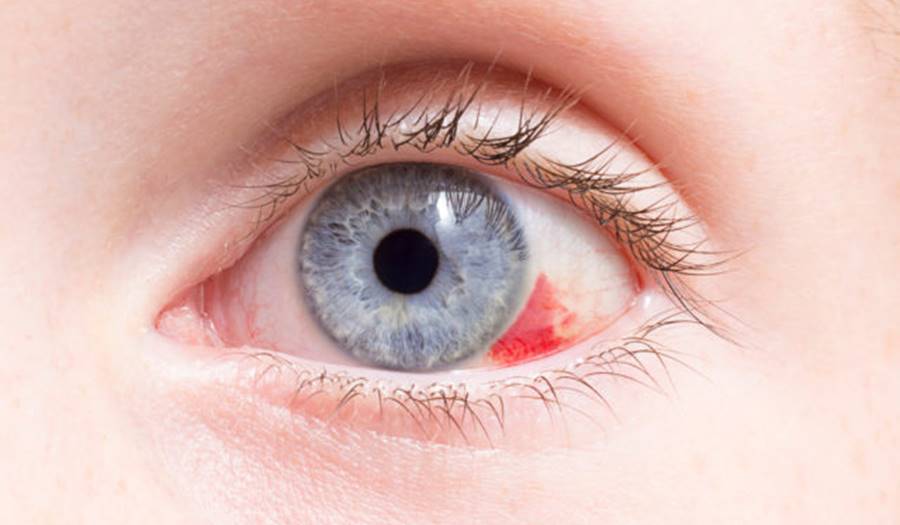
Subconjunctival hemorrhage
A subconjunctival hemorrhage is when there is bleeding, which appears as a red patch, in the sclera (the white part of your eyes) beneath the clear lining of the eye, the conjunctiva. It can happen due to trauma or a foreign object enter the eye. It can also be the result of injury from heavy lifting, straining, vomiting, rubbing eyes too hard, or even a severe sneeze. We even see this in a baby’s eyes after delivery. Generally, this is painless and causes no vision changes or eye discharge. It will improve over a 2-week period.
Corneal abrasion
A corneal abrasion is a scratch on the cornea caused by a foreign body including dirt, leaves, metal shavings, paper, and fingernails. The cornea the clear part of the eye that cover the pupil the iris and the front of the eye. A corneal abrasion is very painful and causes tearing, constant blinking, or the need to keep the eye closed. If you suspect your child might have a corneal abrasion, it should be evaluated. Untreated it can result in infection or a corneal ulcer.
We diagnose corneal abrasion in our office using a fluorescein exam. During this exam we put ab eye drop into the eye that contains dye. We make the room dark then use a black light to see if the dye “pools” in the abrasion. The area will often be treated with an antibiotic ointment. Patching the eye can help let the eye rest and provides some comfort. We will reexam the eye in 24-48 hours. Often the eye if fully healed in that time.
Hyphemia
Hyphemia is an injury to the eye due to blunt trauma. It is very serious eye injury. It causes blood to collect in the front of the eye between the cornea (the front clear surface) and the iris (the colored part of the eye). A hyphemia may cause eye pain, blurred vision, loss of vision, photophobia, or light sensitivity. Sometimes the accumulated blood is visible across the iris.
This type of injury should be evaluated by an ophthalmologist to check to make sure there is no additional injury including damage to the retina, a cataract or other blood collecting. Treatment is based on symptoms and complications but usually includes bed rest with the child’s head elevated and limited activity for a few days. They eye will also be protected with a shield and steroids eye drops. Pain-relieving eye drops may be used. If the blood does not clear or the pressure inside the eye increases surgery may be required.
Globe Rupture
A globe rupture or punctured eyeball is an eye emergency. It is the result of a sharp object tearing the cornea or sclera and can result in permanent vision loss. The eye should be protected. Do not apply any pressure. Seek emergency care. Often surgery is required to repair the eye.
Orbital Hematoma
An orbital hematoma is an emergency eye injury that is the result of blunt force trauma. With this type of injury, blood gets inside the orbit (the bone around the eye). This causes compression on the eye that injures the optic nerve resulting in vision loss in as little as 90 minutes. Symptoms include pain, vision loss, bloody conjunctiva discharge, and proptosis (when the eyeball is pushed forward). Diagnosis is often done via the emergency room and often involves labs and a CT scan and then emergency surgery.

EYE LUMPS, BUMPS AND DISCHARGE
Conjunctivitis
There are three type of conjunctivitis each with its’ own cause and treatment. Conjunctivitis is inflammation of the conjunctiva, the outer membrane of the eyeball and inner eyelid.
Bacterial conjunctivitis is an infection of this membrane and results in purulent discharge from the eye. This is a contagious infection. It can affect one or both eyes. It is treated with eye antibiotic drop or ointment.
Viral conjunctivitis is inflammation due to a viral infection. This results in pinkness to the white of the eyes and a watery discharge. This often is in both eyes and resolves on its own in a few days.
Allergic conjunctivitis is due to allergens causing inflammation of the conjunctiva. These can include pet dander, pollen, or mold. Even toddlers can have allergic conjunctivitis. This usually results in watery or whitish eye discharge. This is treated with an oral antihistamine or allergy eye drops.
Eyelid Swelling
Eye lid swelling has many causes. If one eye is swollen potential causes include rubbing, an insect bite, contact dermatitis, injury, conjunctivitis, an eyelash infection, or a tear gland infection. It may also be from sinusitis, pre-septal cellulitis, or orbital cellulitis. If both eyes are swollen, the potential causes can include conjunctivitis (bacterial, viral, and allergic) and if your child has an allergic reaction.

Bites, Contact Dermatitis and Allergic Reactions
Bites, skin reactions to irritants and allergic reactions can result in significant eye swelling. The face is a vascular area meaning there is a large amount of blood in this area. When eyelids are irritated a lot of fluid arrives to a small area. The eye is also a dependent area. That means when we lie down, the swelling can’t get over the bones surrounding our eye and will pool there and look much worse when you wake up! The best treatment for bites, contact dermatitis or allergic reactions is an antihistamine such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl) or cetirizine (Zyrtec), keeping your child upright as much as possible, and applying ice or cool compress.
Cellulitis
Cellulitis of the eyelid or the skin around the eyelid is a very serious infection called pre-septal cellulitis. It results in red, swollen, and tender skin. It may cause swelling and the eye may swell shut. It is usually only seen on side of the face or one eye. Fever can occur but isn’t necessary for diagnosis. This type of cellulitis can occur spontaneously or due to untreated bacterial conjunctivitis or sinusitis. This requires oral antibiotics and frequent monitoring to evaluate the infection.
A more significant infection is orbital cellulitis. Orbital cellulitis can be due to a wound or the spreading of another infection such as sinusitis or a mouth infection. This means the tissues in the orbital septum are infected which due to the proximity to the eye can cause vision loss. Symptoms include swelling and redness of the eye lid, bleeding of the conjunctiva, chemosis (swelling of the conjunctiva), decreased ability to move the eye or pain when moving the eye. Vision can also be reduced or blurred. The eye may be pushed forward due to the swelling. This type of infection requires hospitalization for antibiotic treatment and monitoring. It may also require surgery to relieve pressure or to drain infected material.
Stye
A stye, also known as a hordeolum, is a painful red lump on the eyelid due to an infected oil gland near the eyelashes. These are treated with warm compresses. If that doesn’t resolve the stye an antibiotic eye ointment may be needed. Recurrent styes should be evaluated by an ophthalmologist.
Blepharitis
Blepharitis is the inflammation of the oily glands of the eyelid. It can cause swollen eye lids and crusting just at the eyelash. Treatment includes warm compresses and washing the area with baby shampoo. Sometimes an antibiotic is necessary.
Chalazion
A chalazion is a firm bump on the eyelid due to a blocked oil gland. It is usually painless and will resolve on its own. You may use a warm compress. Occasionally eye drops or surgery are needed but this is rare.
Eye health is important to protect your vision. Eye injuries and persistent eye symptoms require evaluation by your provider or an ophthalmologist to ensure that the injury or condition does not affect vision. If you have concerns about your child’s vision or eye health, please ask your provider to evaluate and provide treatment recommendations.
Children’s Health Care of Newburyport, Massachusetts, and Haverhill, Massachusetts is a pediatric healthcare practice providing care for families across the North Shore, Merrimack Valley, southern New Hampshire, and the Seacoast regions. The Children’s Health Care team includes pediatricians and pediatric nurse practitioners who provide comprehensive pediatric health care for children, including newborns, toddlers, school-aged children, adolescents, and young adults. Our child-centered and family-focused approach covers preventative and urgent care, immunizations, and specialist referrals. Our services include an on-site pediatric nutritionist, special needs care coordinator, and social workers. We also have walk-in appointments available at all of our locations for acute sick visits. Please visit chcmass.com where you will find information about our pediatric doctors, nurse practitioners, as well as our hours and services.
Disclaimer: this health information is for educational purposes only. You, the reader, assume full responsibility for how you choose to use it.








